Answer
Dear Sarah,
A resultant force is the force that is the “sum of the different force vectors” acting on an object/body.
A force is represented in physics as a vector because in addition to a magnitude it also has a direction and a meaning. Take gravity, for example, and the scale will give you the magnitude, the direction is vertical, and the sentence is downward. Now let’s put that into practice:
You are on a flat surface. Then 2 forces act on you
1) gravity (so you don’t fly away): pulls you down vertically
2) normal force (counteracting force between the ground and your feet that keeps you from sinking into the ground*): pushes you up vertically.
Because you do not fly away or sink into the ground, we know that you are in “rest”, and therefore no “force acting on you” (in this context, “force” always means the resulting force). I know this is a bizarre formulation, but that’s probably how you get it in physics class :-). The resultant force is zero, so the normal force and gravity are the same.
fres=Fzw+Fnorm=0
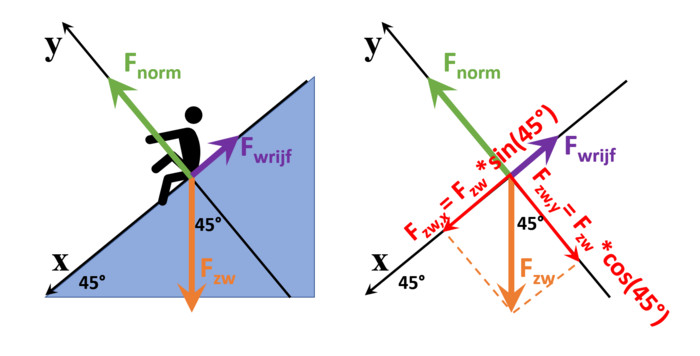
Let’s make life a little more complicated and put you on a slope with ice on it. Then there are 3 forces at work: (see figure)
1) gravity straight down
2) Normal force perpendicular to the slope
3) frictional force in the direction of the slope.
I choose a slope with an angle of 45°, so that the cos(angle)=sin(angle)=root(2)/2 which we call “A”.[dit is om mijn rekenwerk te vereenvoudigen]
Since the forces are not in the same direction, we will decompose them into their components. For this we choose a cross-axis with the x-direction along the slope, with + in the direction of downhill. The y direction is then perpendicular to the slope, with the + pointing up.
When you slide down we can say the following about the forces:
the x components: (on the right side of the equal sign, Fx always stands for the size of the vector)
frub,x=-Frub
fnorm,x=0
fbw,x=Fzw*A
the y components:
frub,y= 0
fnorm,y=Fnorm
fzw,y=-Fzw*A
The resulting force then becomes:
fres,x= Frub,x +fnorm,x + Fbw,x = -Frub + Fzw*A
fres,y= Frub,y +Fnorm,y + Fzw,y = Fnorm – Fzw*A = 0 (this because we know you won’t sink through the ground 🙂 )
and the magnitude is then the length of this vector:
fres=root( Fres,x*Fres,x + Fres,y*Fres,y )
I hope this gives you some clarification.
Regards,
Danny
(* The cause of this normal force is the coulomb force with which the atoms from your feet repel the atoms from the ground)

Answered by
dr. Danny Vanpoucke
Computational Materials Research

Agoralaan University Campus Building D BE-3590 Diepenbeek
http://www.uhasselt.be/
.