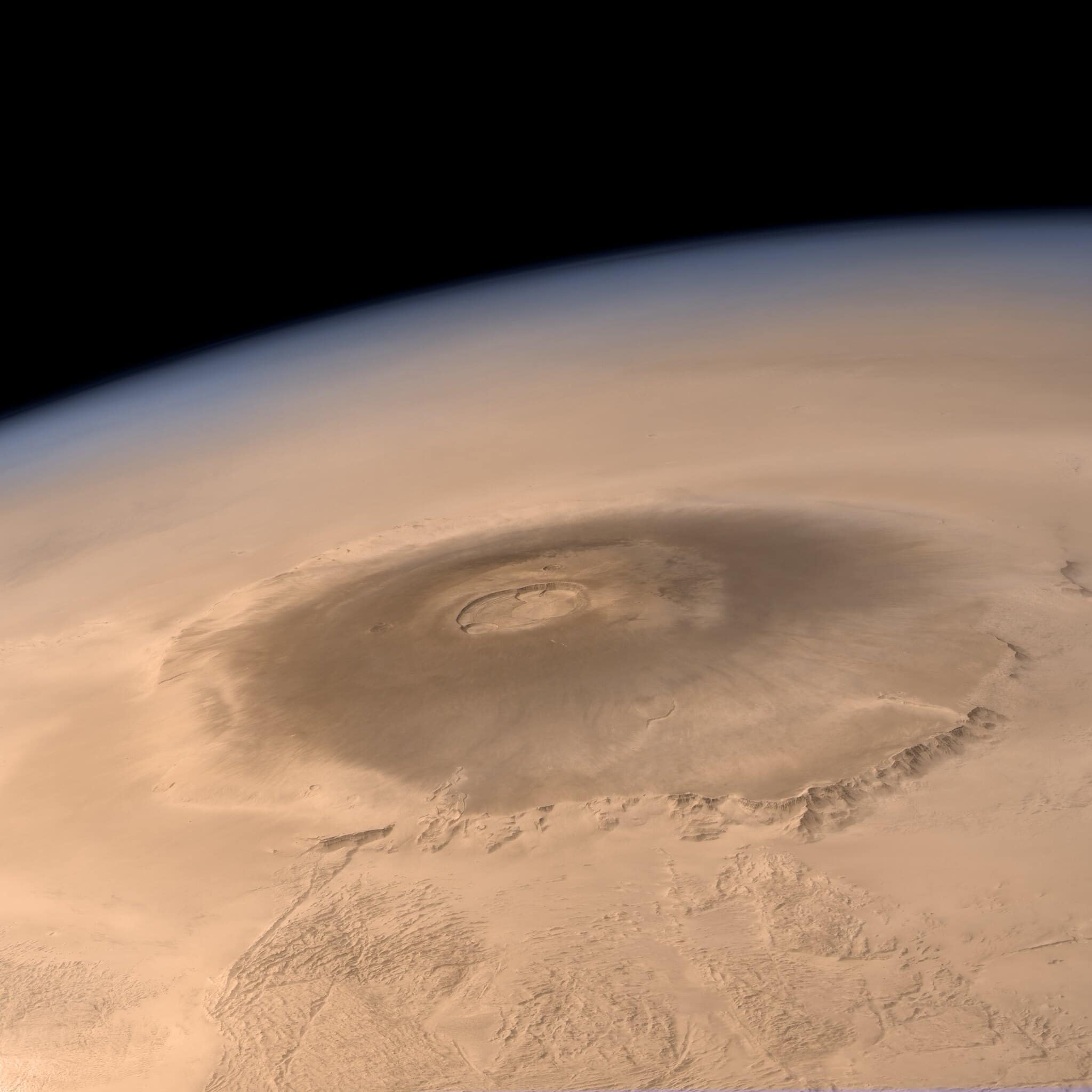
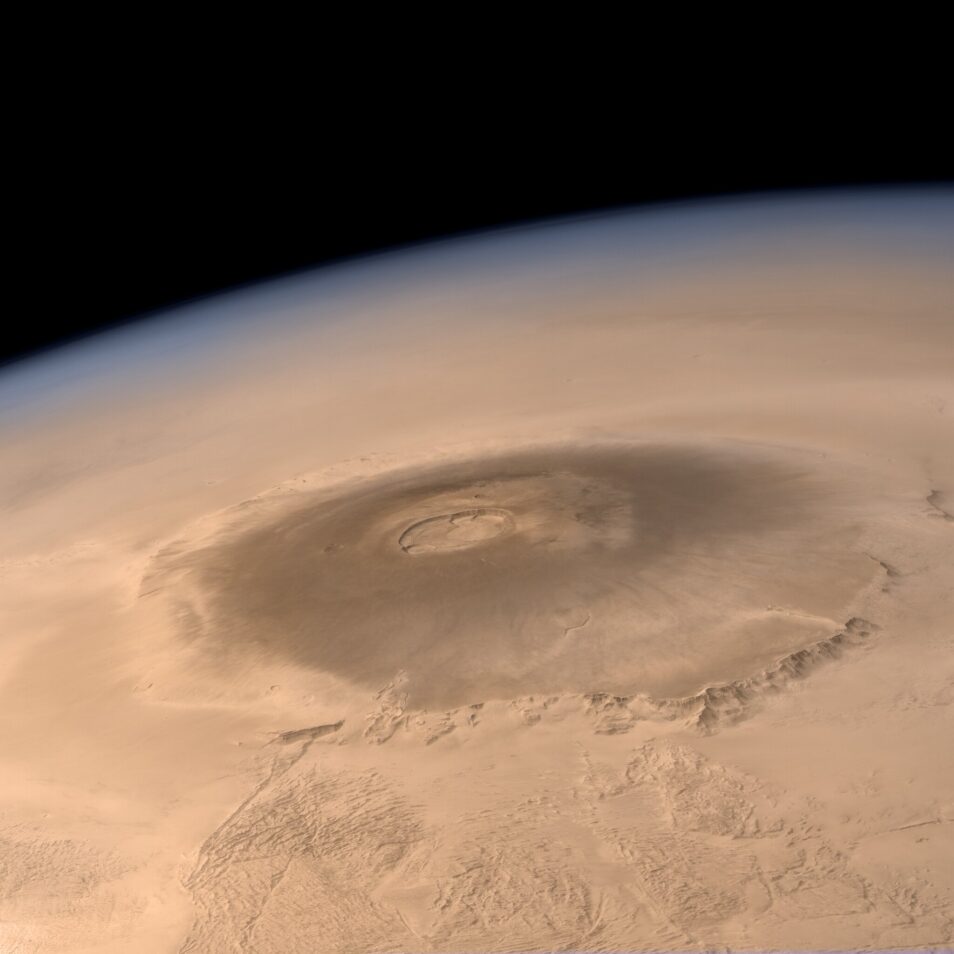
If you fly past the planet Mars in a spaceship, you will probably notice a huge boil. This is Olympus Mons: the largest and highest mountain in the solar system. This gigantic shield volcano has a height of 26 kilometers.
Mars is regularly ravaged by huge dust storms, through which the tops of the Tharsis volcanoes pierce. At those times, the volcanoes are clearly visible from Earth. As a result, Olympus Mons was spotted by astronomers as early as the nineteenth century, such as by the Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli† In the 1970s, the Mariner 4 probe flew past Mars and for the first time we got sharp images of the shield volcano.
The shield volcano is more than a hundred million years old, but scientists aren’t sure how old it is. Not many impact craters are visible, so that’s a sign that the surface is very young. The last major eruption was probably 25 million years ago, although lava may have flowed over the volcano two million years ago† Since Mars is 4.5 billion years old, this means that the volcano was active quite recently. During an eruption, lava flows over the area around the volcano. The lava solidifies, causing the volcano to grow slightly larger again. So the volcano continues to grow.
The large bowl-shaped crater on top of the volcano – the so-called caldera – measures 65 by 80 kilometers. Several pit craters can be seen in this caldera, of which the deepest crater is three kilometers deep.
The space photo of the week is the photo below from the Mars Express. The European spacecraft took this photo on March 10, 2010 at an altitude of 4,000 kilometers above the surface of the red planet.

Olympus Mons vs Mount Everest
As a shield volcano, Olympus Mons is more similar in shape to the large volcanoes that make up the Hawaiian Islands than the Himalayas. The Olympus Mons volcano has a much larger surface area than Mount Everest and is about the same size as Poland with an area of 300,000 square kilometers. If you want to climb this shield volcano, the journey from foot to top takes 300 kilometers. With an average slope of 5%, this volcano is not too much of a challenge for the inexperienced climber. However, 5% is an average of course. The shield volcano has the shape of a circus tent, which means that there are also tricky parts, such as steep walls at the beginning.

Compared to Mount Everest, the Olympus Mons is a huge giant.
Suppose you are on top of the Olympus Mons, then you cannot see a large part of the mountain. Olympus Mons is so large that a large part of the volcano disappears behind the horizon because the planet is round. So you do not realize that you are standing on a high volcano. You won’t see this until you walk back to the edge.

Olympus Mons is shaped like a circus tent. This is clearly visible on this elevation map.
Why is Olympus Mons so big?
Olympus Mons is much larger than shield volcanoes on Earth. This is probably because Mars has no plate tectonics. The crust of Mars is solid, creating a fixed hotspot. A volcano here continuously releases lava and thus reaches an enormous height.
The shield volcano is not a good landing spot for Mars rovers and landers. The volcano is so high that the atmosphere is very thin. This will prevent a spacecraft with a parachute from slowing down fast enough and will likely crash into the volcano.
If we ever want to know more about the history of the volcano, it can be interesting to fly a drone over the volcano.
Source material:
Image at the top of this article: Mars Express (ESA)