
A new ‘version’ of Windows 11 is coming with Windows 11 24H2. Are there any major changes coming and what functionality will be added? We give you a glimpse of the veil.
Ger Stok
Usually around this time the author (and not just him) starts to get itchy. The first announcements are made about the upcoming release of Windows 11 and these adjustments can often already be found in the Insider version of Windows. We will review a few things here, starting with artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
 It is clear that Microsoft has already invested heavily in AI in recent times. The company will expand this even further. Unfortunately, many of these innovations are only partially available for existing computers. The real power is only released with – what Microsoft calls – a CoPilot+ computer. This does require new hardware. To this end, a series of laptops and PCs with new processors will be launched this year, equipped with an NPU (Neural Processing Unit). From Qualcomm this will be the Snapdragon X series, from Intel the Core Ultra (Lunar Lake) and from AMD AI 300 and 9000 series (Strix Point). In addition, the requirement also applies that the NPU has at least 40 TOPS (40 Trillion Operations Per Second) can perform. The AI operations are then no longer mainly performed online, but locally. This has major advantages for applications such as image and video editing (Studio effects) that go much further than just removing or blurring a background, and CoCreator where an image can be created based on typed or spoken directions and the successor to TimeLine, called ReCall . The latter is the Activity History in the form of Snapshots and keeps track of what work you have done on the computer recently.
It is clear that Microsoft has already invested heavily in AI in recent times. The company will expand this even further. Unfortunately, many of these innovations are only partially available for existing computers. The real power is only released with – what Microsoft calls – a CoPilot+ computer. This does require new hardware. To this end, a series of laptops and PCs with new processors will be launched this year, equipped with an NPU (Neural Processing Unit). From Qualcomm this will be the Snapdragon X series, from Intel the Core Ultra (Lunar Lake) and from AMD AI 300 and 9000 series (Strix Point). In addition, the requirement also applies that the NPU has at least 40 TOPS (40 Trillion Operations Per Second) can perform. The AI operations are then no longer mainly performed online, but locally. This has major advantages for applications such as image and video editing (Studio effects) that go much further than just removing or blurring a background, and CoCreator where an image can be created based on typed or spoken directions and the successor to TimeLine, called ReCall . The latter is the Activity History in the form of Snapshots and keeps track of what work you have done on the computer recently.
Furthermore, the retrieval options have been greatly improved. Voice commands can now also be used to recall activities. That may be a useful option for some, but it seems quite privacy-sensitive to me.
Another example of the new expansion is that live subtitling of films and videos in forty languages is now also possible. Future games will also benefit from AI applications such as Auto Super Resolution. The NPU assists in rendering scenes, the image becomes significantly sharper, makes higher frame rates possible and also relieves the burden on the graphics card.
The latest generation of video cards are also equipped with an NPU chip, but whether this only works for image processing or also with all other general AI applications within version 24H2 is still unclear.
CoPilot
 CoPilot is available as a standalone app in a number of language areas (English, Spanish, French and German) and will also be available in Dutch with the upcoming upgrade. But so far there has been little sign of this. But just wait until the eventual launch of the upgrade. Speaking of that upgrade, it is more extensive than we were used to from previous versions, including a new kernel. The upgrade will therefore take more time.
CoPilot is available as a standalone app in a number of language areas (English, Spanish, French and German) and will also be available in Dutch with the upcoming upgrade. But so far there has been little sign of this. But just wait until the eventual launch of the upgrade. Speaking of that upgrade, it is more extensive than we were used to from previous versions, including a new kernel. The upgrade will therefore take more time.
 |
Adjustments to the Explorer
Compression and decompression – As of version 2023H2, it became possible to extract files in 7zip and tar format in addition to zip files. The possibilities are now being further expanded. Compression to 7zip and tar is also possible. This is very pleasant for those who also work with Linux files, because tar compression is often used there.
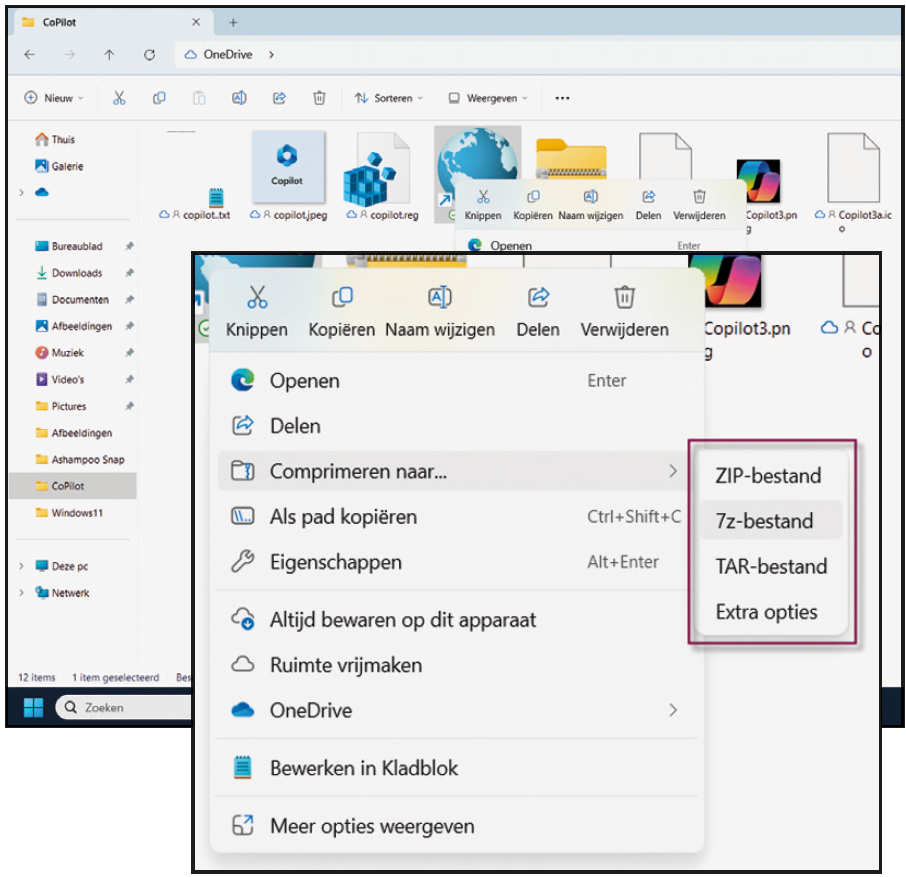 |
| Now compression in 7z and tar formats is also possible |
Cosmetic procedure – Until now, when you right-clicked on a file or folder, you were presented with a number of icons for copying, cutting, etc. That was apparently not clear enough, so text labels have now also been added to the icons. Not earth-shattering, but still…
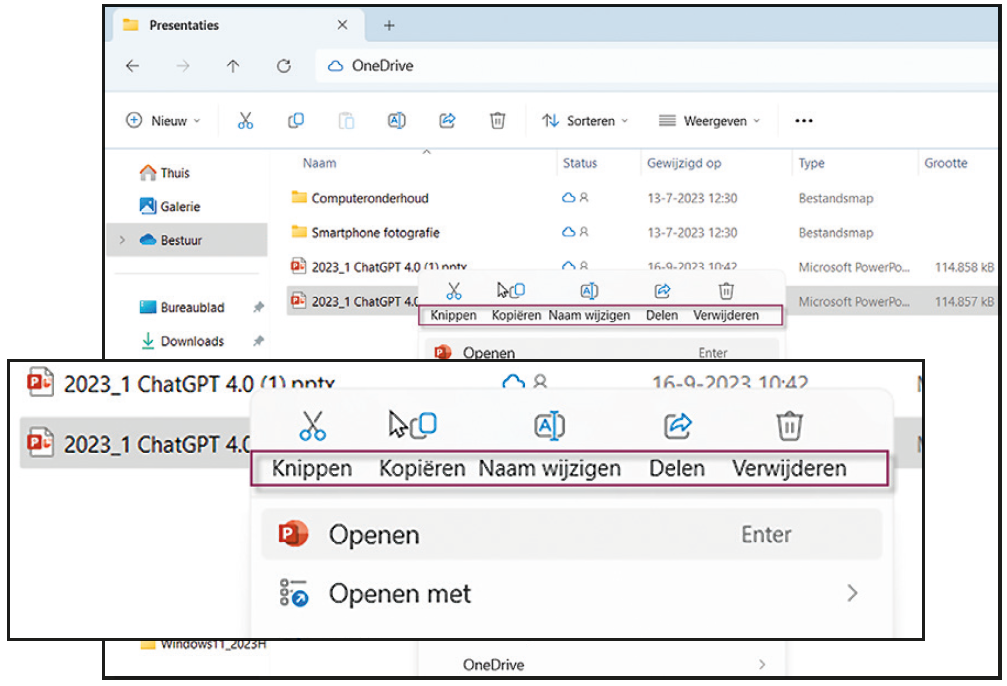 |
| Not only icons but also text labels for clarification |
WiFi
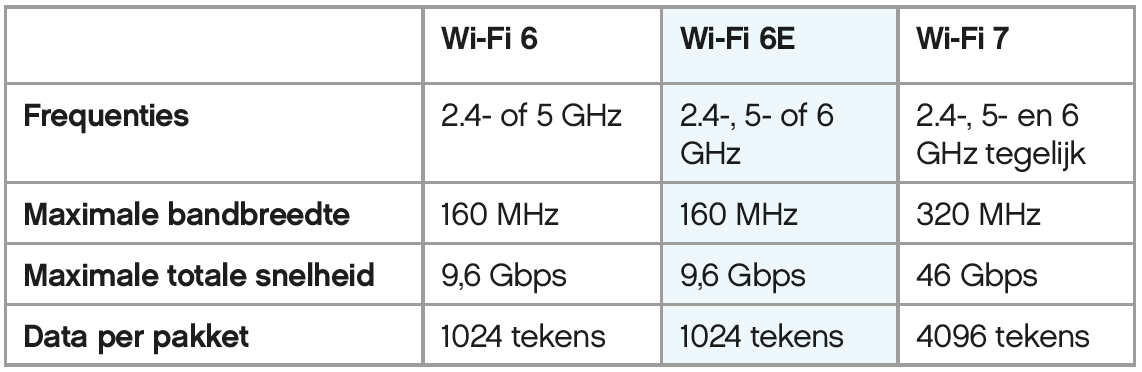
This version will officially support Wi-Fi 7. The requirement is that all components, such as routers, network cards/chips, etc., support this Wi-Fi 7 protocol.
The speed gain is astonishing, from a maximum of 9.6 Gbps (Wi-Fi 6E) to 46 Gbps (see table below), but it does come with a hefty price tag.
COMPARISON WIFI 6, WIFI 6E AND WIFI 7
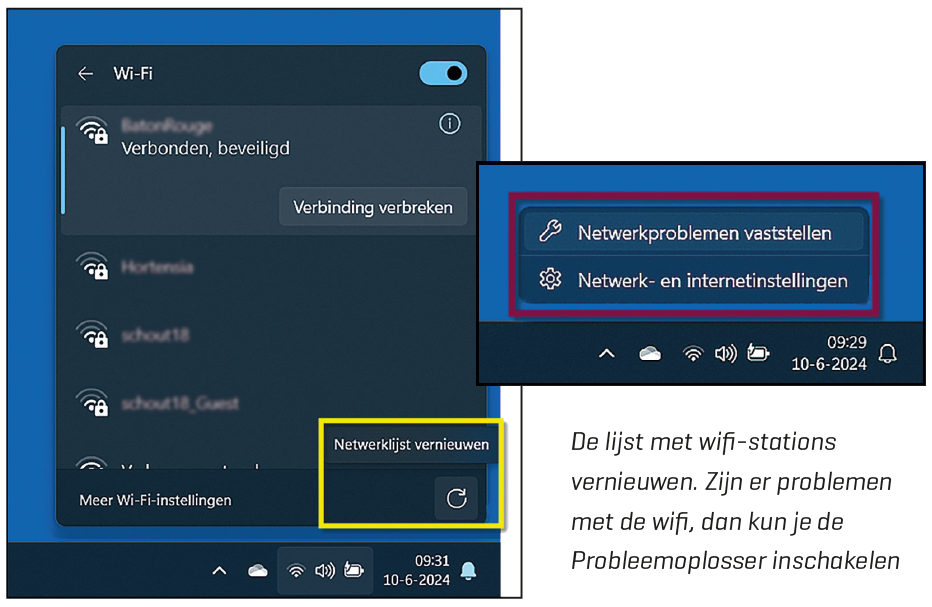
The WiFi settings have also been addressed on a number of points. This way you can easily refresh the list of WiFi stations and if there are problems with the connection, the updated one can be used Problem solver be called quickly.
 |
Sudo (for Windows)
Sudo (SuperUser Thu) is a well-known concept in the Linux world. It is used there in a Terminal window to allow the command line to be run as admin. If you want to achieve the same thing in Windows, you need to use the Terminal or Powershell open with administrator rights. That is no longer necessary. A command line preceded by Sudo is executed at the admin level. Of course you will be asked for confirmation.
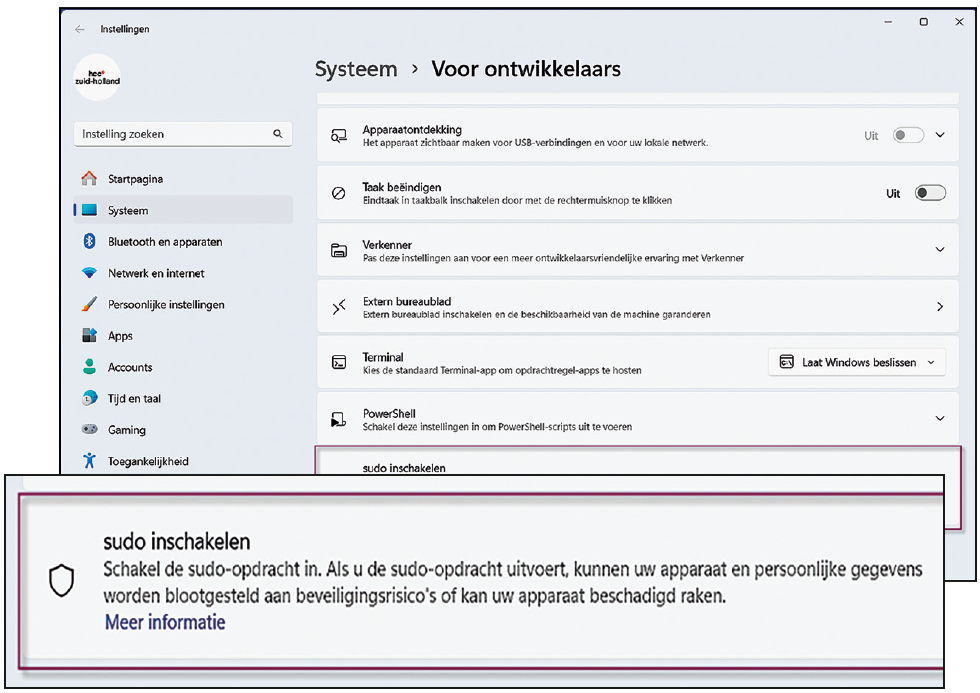 |
| Sudo must be enabled first Institutions |
Energy management
While there used to be differences in the setting options of a battery-powered device (laptop/tablet) and a desktop computer, that distinction has now disappeared. Both now have an extensive set of setting options to reduce power consumption, or – as Microsoft propagates – to contribute to CO2-reduction. Keep in mind that lower power consumption also affects the overalls-system performance. The condition and consumption of the battery over the past period can now also be visualized. The behavior of the power button, the lid of the laptop and the times when the computer should be put to sleep are now easier to set.
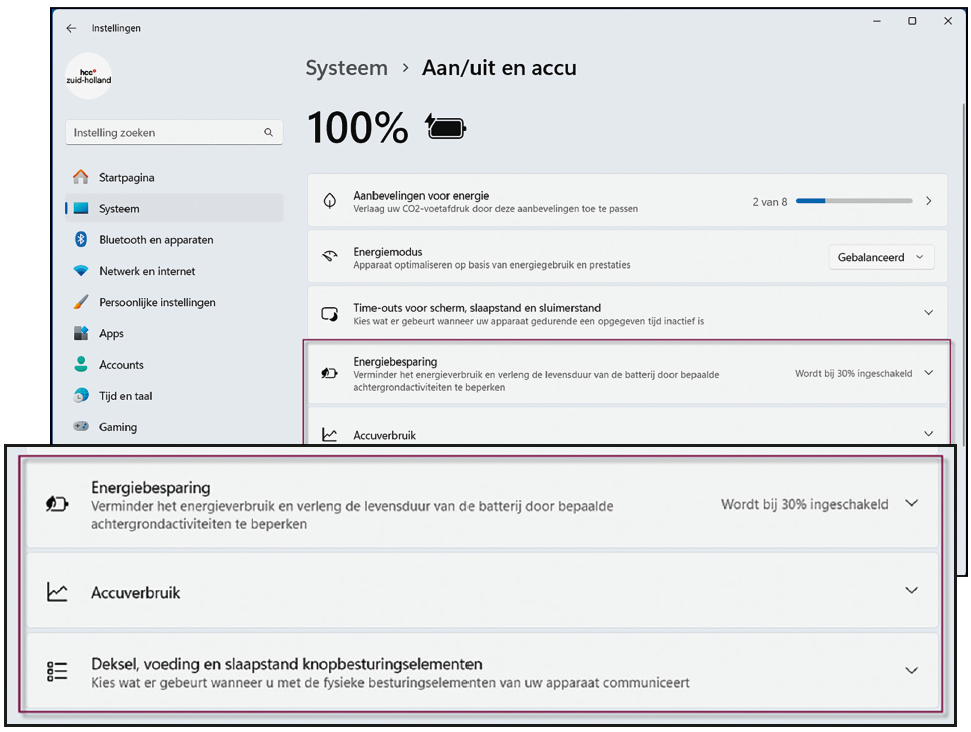 |
| Energy management has been further expanded, also for devices without a battery |
Smartphone link
In version 23H2 it was already possible to connect the smartphone to Windows so that all kinds of things were synchronized on multiple systems. With the arrival of the new version it is also possible to use the smartphone as a webcam. This can be done not only wired but also wirelessly, increasing the number of possible applications. But unfortunately it remains exclusively about Android smartphones. Sorry Apple.
 |
| Your (Android) smartphone as an autonomous webcam |
Quick settings
By clicking on the bottom right of the taskbar we can call up some quick settings. A limitation is that we can only visualize six of these settings. This has been adjusted in the new version of Windows. Although we still only get six on screen, there is a scroll button on the right side with which we can view the other settings.
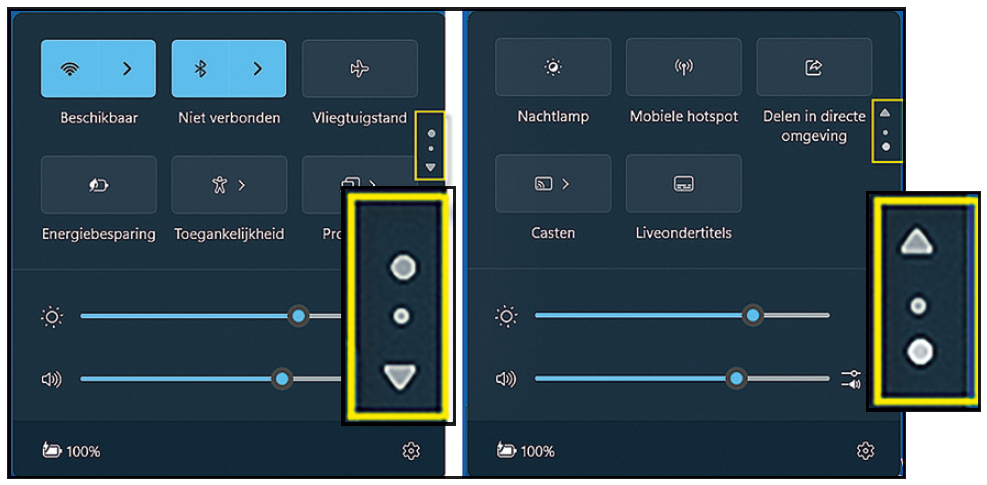 |
| The number of visible Quick settings is still six, but you can now scroll to view the others |
Support USB4
The new version now officially supports USB4 2.0. Maximum transfer speeds are 40 Gbps for USB4 1.0 and 80 Gbps (bi-directional) or 120 Gbps (uni-directional) for USB4 2.0, a big step forward compared to USB3.2. The requirement is that USB4 equipment with a USB-C connection and PD (Power Delivery) is used.
If you have such USB4 devices, you can also set this up Settings > Bluetooth & devices > USB > USB4 Hubs & devices.
 |
| The various USB versions with their associated maximum speeds |
Drivers and more
There’s a new one printerstack available that can work with a protected print mode. This requires a new generation of printer, the so-called Mopria printer. Additional advantage: they work immediately without having to install third-party drivers.
With a new/clean installation, the option is now also offered to install the drivers for various devices, for example WiFi, during the installation. You do not have to wait until the installation is completely completed.
 |
| Mopria printer… just connect and print |
Disappearing apps
With a clean installation of version 24H2, the apps are installed by default Cortana, Mail, Calendar and Cards no longer installed. If you still want to use it, that’s no problem. They can easily be reinstalled via the Windows Store.
Windows on ARM machines
As of this version, support for 32-bit ARM processors will no longer be available. Only the 64-bit version remains and is actively maintained. While everyone is eagerly awaiting the end date for Windows 10 support, the curtain has fallen even earlier on this type of ARM machine.
Windows 11 on an uncertified machine
Although it has so far been possible to install Windows 11 on a machine that does not meet the minimum system requirements with a number of tricks, there is now an additional barrier. If the processor does not support POPCNT (Population Count), part of the instruction set SSE4.2 (Intel) or SSE4a (AMD), the machine will no longer be able to run Windows 11 24H2. boating. This generally concerns Intel processors from before 2008 and AMD processors from before 2011. It does not look like a solution will be found for this quickly. So for these machines: Goodbye Windows, hello Linux.
And what about Windows 12?
Most of the innovations/adjustments we discussed here were reserved for Windows 12, but that release has been shelved for the time being. It seems that Microsoft does not want to actively maintain more than 2 SKUs (Windows versions). So Windows 12 may appear after Windows 10 support ends. Or will Windows 10 support be extended?
Finally
As always, Microsoft remains Microsoft. I wouldn’t be surprised if some things are left out or that another surprise is pulled out of the hat when the final release of Windows 24H2 is released this fall. It remains to be seen.
|
Thanks to Martin Bekelaar for his input. |