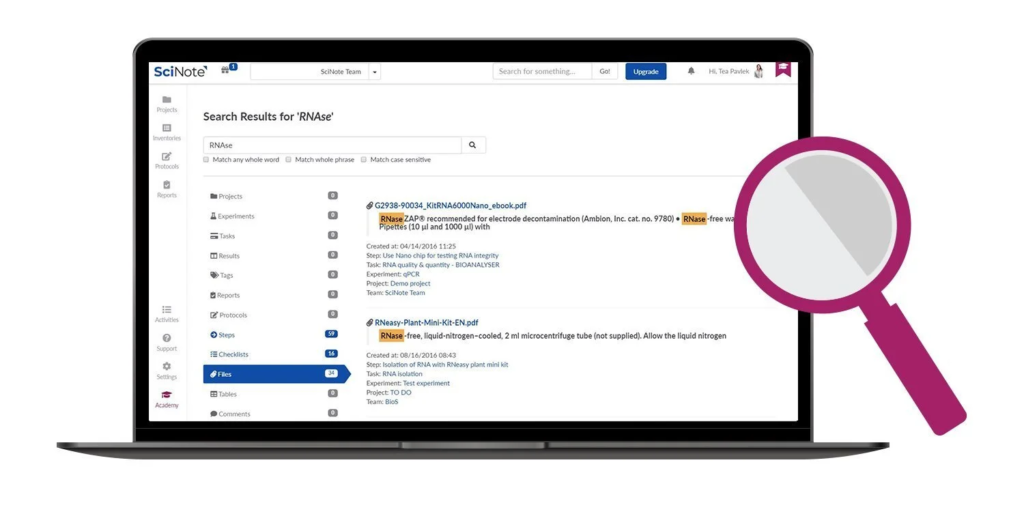
In the dynamic landscape of modern laboratories, the utilization of technology has become paramount in streamlining research processes and data management. One such technological advancement is the Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) software, which has revolutionized the way laboratories record, organize, and share information. As laboratories transition from traditional paper-based methods to digital solutions, the choice of the right ELN software emerges as a critical decision. This article delves into the intricacies of selecting the best ELN software for your lab, exploring the distinction between ELN and LIMS systems, while also providing insights into the key factors to consider during the selection process. By understanding the core functionalities and best practices, laboratories can make informed decisions that optimize efficiency, collaboration, and the overall research experience.
ELN vs LIMS: Understanding the Difference
In the realm of modern laboratory management, technological advancements have introduced transformative tools that not only enhance research processes but also streamline data management. Two such powerful solutions that have gained prominence are the Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) and the Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS). While both ELN and LIMS contribute significantly to the efficiency of laboratory operations, it’s essential to understand the distinction between ELN vs LIMS to make well-informed decisions about which system best suits the unique needs of your lab.
Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN)
At its core, the Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) functions as a digital platform that allows researchers and scientists to seamlessly record, organize, and share their research activities and findings. It represents a digital evolution of the traditional paper laboratory notebook and offers an array of advantages that are particularly pertinent in the digital age.
- Data Recording and Documentation: The central focus of ELN revolves around efficient data recording and meticulous documentation. Researchers can input intricate experiment details, protocols, observations, and results in a structured digital format, facilitating not only easy access but also swift retrieval for future reference.
- Collaboration and Sharing: ELN goes beyond just recording data; it is designed to facilitate collaboration among researchers. The real-time sharing of experiments and data enables team members to collaborate seamlessly regardless of geographical locations, fostering enhanced teamwork and knowledge sharing.
- Flexible and Adaptable: ELN systems are engineered with flexibility in mind. Researchers can mold the software to suit their specific workflows and methodologies, ensuring that the tool complements their unique research practices.
- Data Security: Given the sensitivity of research data, ELNs prioritize data security. They often incorporate robust encryption and access controls to safeguard valuable intellectual property and confidential information.
Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS)
On the other end of the spectrum, the Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is meticulously designed to manage and streamline diverse aspects of laboratory operations, transcending individual research activities.
- Sample and Data Management: LIMS excels in the management of samples and data. It offers meticulous tracking of samples from their point of collection through to analysis, ensuring accurate documentation and minimizing the potential for mix-ups.
- Workflow Automation: One of the key strengths of LIMS is its ability to automate workflows. By standardizing processes, from sample registration to reporting, LIMS significantly reduces manual errors and enhances overall efficiency in the lab.
- Instrument Integration: LIMS seamlessly integrates with various laboratory instruments, allowing for direct data capture. This integration not only streamlines data collection but also minimizes the risk of transcription errors.
- Regulatory Compliance: LIMS often comes equipped with features that facilitate adherence to regulatory compliance standards. This makes it an optimal choice for laboratories operating in regulated industries where compliance is paramount.
- Advanced Analytics: Beyond data management, LIMS offers analytical tools that empower users to extract valuable insights from accumulated data. This capability aids in informed decision-making and contributes to the lab’s overall efficiency.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Lab
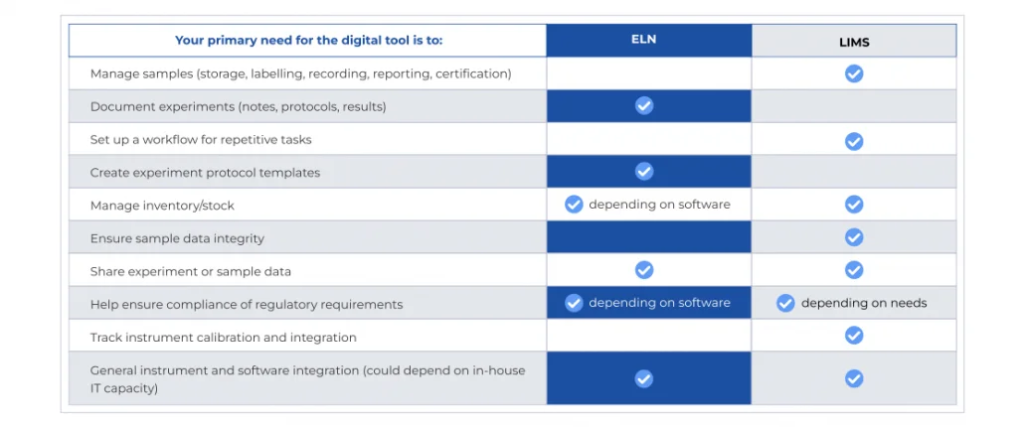
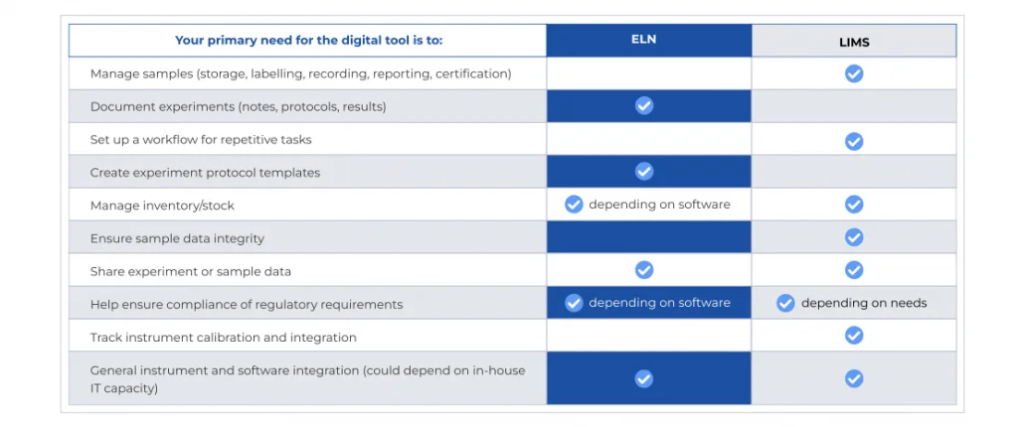
The decision to opt for ELN or LIMS hinges on a thorough understanding of your lab’s unique needs and objectives.
- Choose ELN If: If your lab’s primary requirement revolves around efficient data recording, collaboration, and the seamless sharing of research insights among team members, then ELN is a fitting choice.
- Choose LIMS If: Alternatively, if your laboratory manages a substantial volume of samples, operates intricate workflows, and requires robust sample and data management, LIMS emerges as the ideal solution. It is particularly well-suited for labs that seek to streamline processes, automate workflows, and ensure adherence to compliance standards.
Factors to Consider When Choosing ELN Software
In the quest to enhance laboratory efficiency and data management, selecting the right Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) software becomes a pivotal decision. To ensure that the chosen software aligns seamlessly with your lab’s operations and research needs, it’s imperative to take into account a range of factors that contribute to its functionality, usability, and long-term value. Here are the key factors to consider when choosing ELN software:
1. User-Friendly Interface and Accessibility
- An Intuitive Interface: The user-friendliness of the ELN software is essential for smooth adoption. A well-designed, intuitive interface ensures that researchers can navigate the software with ease, leading to quicker integration into their daily routines.
- Device Compatibility: Accessibility across various devices is crucial for a modern lab environment. Look for ELN software that supports desktops, tablets, and mobile devices, allowing researchers to access and update information regardless of their location or device preference.
2. Data Security and Compliance
- Encryption Protocols: Security is paramount when dealing with sensitive research data. Opt for ELN software that employs robust encryption protocols to safeguard data from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Depending on your lab’s focus and industry, ensure that the ELN software complies with relevant regulations such as FDA guidelines, HIPAA, and data protection laws. This is especially crucial for labs dealing with sensitive health or patient data.
3. Collaboration and Sharing Features
- Real-Time Collaboration: In today’s globally connected world, real-time collaboration tools are essential. Look for ELN software that enables researchers to collaborate remotely, share insights, and collectively contribute to projects regardless of geographical barriers.
- File Sharing and Annotation: Effective teamwork requires seamless file sharing and annotation capabilities. Choose software that allows researchers to share documents, annotate data, and provide feedback directly within the platform.
4. Customizability and Flexibility
- Workflow Adaptability: Every lab has unique processes and workflows. Opt for ELN software that can be customized to align with your lab’s specific methodologies, ensuring that it enhances your existing practices rather than altering them.
- Integration Capabilities: To avoid disruptions to your lab’s existing ecosystem, select ELN software that seamlessly integrates with your current software systems, such as laboratory instruments and databases.
5. Data Organization and Search Capabilities
- Efficient Data Organization: The ability to organize data effectively is essential for easy retrieval and analysis. Look for ELN software that offers features such as categorization, tagging, and metadata, allowing researchers to structure their data systematically.
- Advanced Search Functions: In a research-intensive environment, time is of the essence. Choose software that provides advanced search capabilities, enabling researchers to swiftly locate specific experiments, results, or notes.
6. Experiment Documentation and Version Control
- Comprehensive Documentation: Thorough documentation is the backbone of research. Opt for ELN software that allows researchers to comprehensively document experiments, protocols, and observations, ensuring that critical details are recorded accurately.
- Version Control: Research evolves, and changes are inevitable. Select software that offers version control, allowing researchers to track changes, revisions, and updates made to experiments over time.
7. Data Visualization and Analysis Tools
- Built-In Visualization: Effective data analysis relies on visualization. Choose ELN software that provides built-in tools for basic data visualization and graphing, facilitating insights from your collected data.
- External Software Integration: For more complex analysis, integration with external analysis software can be invaluable. Ensure that your chosen software supports the integration of advanced data processing tools.
8. Backup and Data Recovery
- Automated Backups: Data loss can be detrimental. Look for ELN software that offers regular automated backups to prevent the loss of valuable research data.
- Data Recovery Mechanisms: Accidental deletions or system failures are possibilities. Choose software that provides efficient data recovery mechanisms to restore lost data promptly.
9. Vendor Support and Training
- Customer Support: Effective customer support is vital for troubleshooting and issue resolution. Opt for ELN software from vendors known for responsive and reliable customer support.
- Training Resources: A learning curve is natural when adopting new software. Ensure that the vendor offers comprehensive training resources and documentation to facilitate effective utilization of the software across your lab team.
Best Practices for Implementing ELN Software
The adoption of Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) software marks a significant step towards modernizing laboratory operations, enhancing data management, and fostering collaboration. However, successful implementation requires a strategic approach that takes into account various factors to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of the software. Here, we delve into comprehensive electronic lab notebook best practices for effectively implementing ELN software in your lab:
1. Develop a Clear Implementation Plan
- Assessment Phase: Initiate the process by conducting a thorough assessment of your lab’s current practices and identifying specific areas that could substantially benefit from the integration of ELN. Gain an in-depth understanding of your lab’s unique needs, workflows, and data management requirements.
- Transition Process: A well-structured implementation plan is paramount. Outline a step-by-step transition process from traditional methods to full-fledged ELN usage. Define roles, responsibilities, and clear timelines to ensure a smooth and organized transition.
- Phased Rollout: Consider a phased rollout strategy as opposed to a sudden switch. This approach allows your lab members to gradually adapt to the new software, providing the space to address any challenges that might arise during the process.
2. Provide Comprehensive Training
- Training Sessions: Deliver thorough and well-structured training sessions to all lab members who will engage with the ELN software. Cover a spectrum of topics including software navigation, effective data entry practices, collaboration features, and other pertinent functionalities.
- Hands-On Practice: Encourage active engagement and hands-on practice to ensure that lab members are not only familiar but also comfortable with the software. Make available training materials, tutorials, and resources that can be accessed as reference points whenever required.
3. Establish Protocols for Data Entry and Documentation
- Data Entry Standards: Establish comprehensive guidelines for data entry to ensure uniform and precise documentation. Specify rules for inputting experiment details, observations, results, and metadata.
- Naming Conventions: Set forth clear naming conventions for experiments, projects, and files. A uniform approach to naming streamlines data retrieval and mitigates confusion.
- Documentation Practices: Emphasize the significance of thorough documentation. Urge lab members to document procedures, protocols, and observations consistently, maintaining a standardized format.
4. Foster Collaboration and Communication
- Communication Channels: Create dedicated communication channels for lab members to facilitate discussions related to projects, share insights, and address questions revolving around the ELN software. This sets the foundation for a collaborative environment.
- Guidelines for Remote Teams: If your lab operates with remote teams, formulate specific guidelines for remote collaboration using the ELN software. Define expectations for communication, protocols for sharing data, and best practices for remote work.
5. Regularly Review and Update Security Protocols
- Security Audits: Regular security audits are essential to assess the software’s existing security measures and identify potential vulnerabilities. This practice ensures the continuous protection of sensitive data.
- User Access Controls: Implement stringent user access controls. Allocate permissions based on roles and responsibilities, curbing any unauthorized access to confidential information.
- Data Encryption: Ensure robust data encryption for information stored within the ELN software. Encryption adds an extra layer of protection, particularly when data is transmitted over networks.
6. Seek Feedback and Continuous Improvement
- User Feedback: Actively encourage lab members to share their feedback based on their experiences with the ELN software. Utilize this feedback to recognize areas for improvement and address any challenges faced by users.
- Continuous Training: Offer ongoing training sessions and refresher courses to keep lab members abreast of software enhancements and new features. This commitment to continuous learning maintains consistent and efficient usage.
Conclusion
The quest for efficient laboratory management has ushered in the era of Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) software, revolutionizing data handling and collaboration. This article’s exploration of ELN versus Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) highlighted their distinct roles: ELN excels in data recording, documentation, and real-time collaboration, while LIMS offers comprehensive sample management, workflow automation, and integration. Selecting between ELN and LIMS hinges on grasping your lab’s unique needs. ELN suits those prioritizing seamless collaboration, while LIMS is for labs handling intricate workflows and compliance. Successful ELN implementation rests on clear plans, comprehensive training, standardized data practices, collaboration fostering, robust security, and continuous improvement. Embracing these practices aligns labs with modern efficiency, collaboration, and innovation trends, propelling their research pursuits forward.