At the end of July, the long-awaited Linux Mint 21 ‘Vanessa’ was released, available for download with three different desktop environments, with Cinnamon being the default environment. How do we use the operating system and ensure that the system continues to function well in the long term?
Peter Brown

When the update to Linux Mint 21 is installed, we should also start using it. During the use phase we come across the following topics: Disk Management, System Management, Menu Manager, Desktop Manager, Program Manager and Data Manager. These topics are discussed one by one in turn
 |
|
Data overview of your disk |
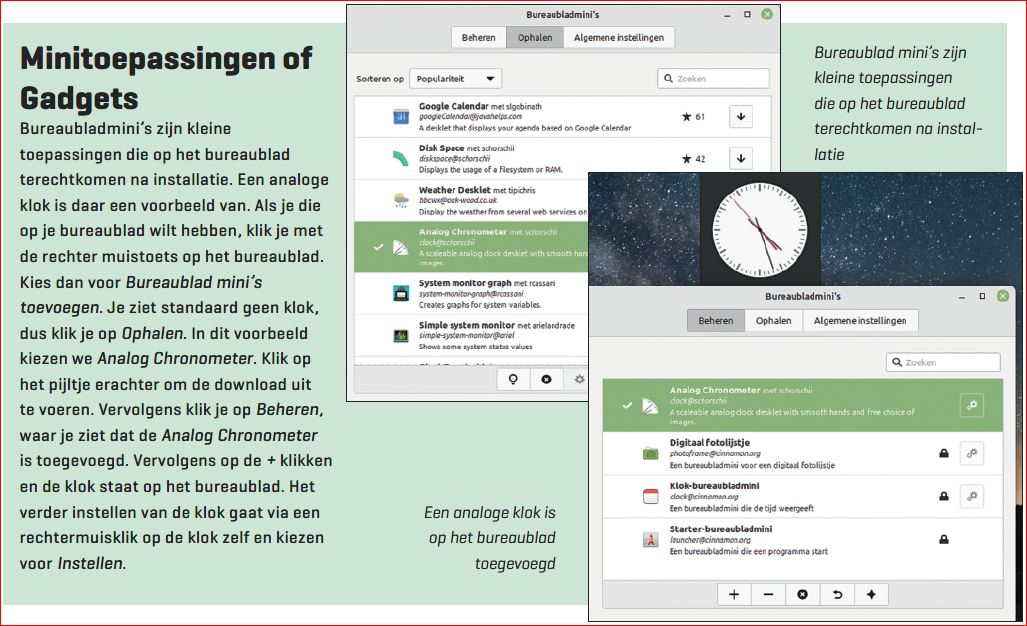
Disk management
During use it often happens that we want to know what the filling is of our storage medium. We then want to investigate whether, for example, there is still enough free space available. Linux has the program for this Disk usage. A colored bar shows how full the storage medium is. A mouse click on this shows further details, which provides more insight into what has been stored. User data can be moved to, for example, an external hard drive when space needs to be freed up.
| Gives a blank shield indicates that the system has been updated |
 |
System administration
By system management we mean all activities to keep Linux operational and that starts with regularly updating the system through the updates offered. If there are updates, the shield in the panel will be colored. A blank shield indicates that the system has been updated.
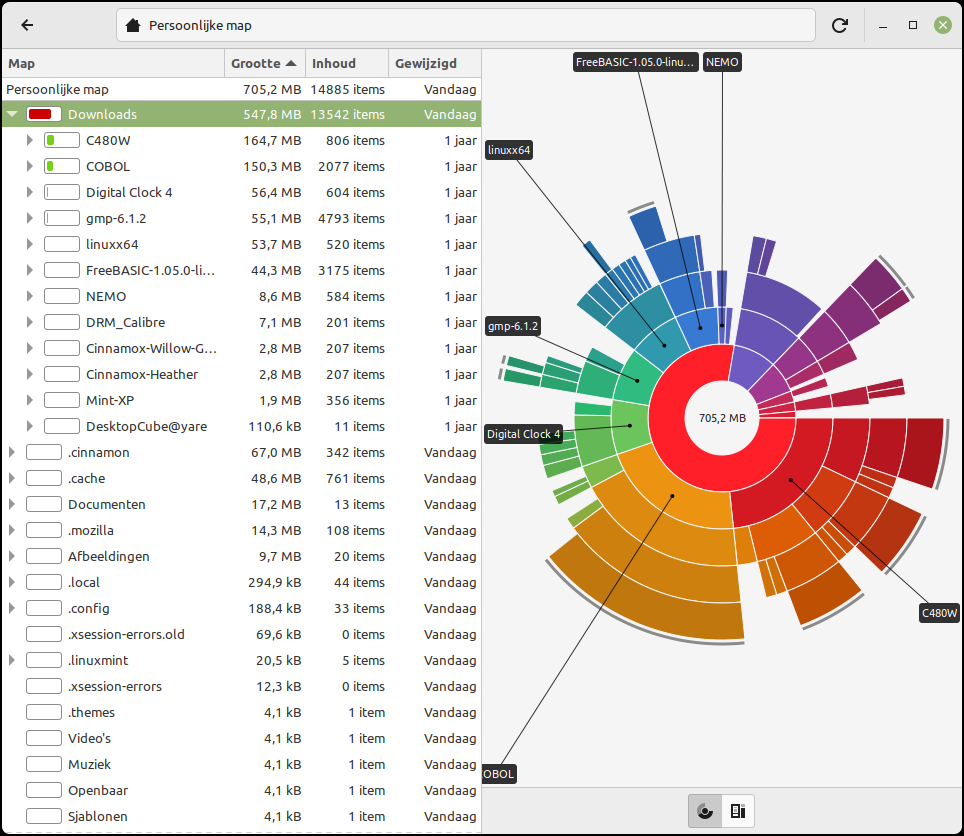
Manage System Core
After longer use and regular updates, new system cores will be added. We can delete the older ones to reclaim disk space. We do this through Administration, Update Manager, Show, Linux Cores. Here’s a warning to handle system cores with care. Get on leads to an overview of installed cores. Remove old system cores then cleans up the system. The current kernel, which is active, must not be deleted.
The process can also be automated, so that you no longer have to worry about it. We do this through Administration, Update Manager, Edit, Preferences, Automation and here then Remove obsolete cores and dependencies check.
 |
|
You can clean up your system via Remove old kernels… |
Backup
It is wise to make a backup of your Linux operating system from time to time. Because if something goes wrong with the system, you can easily go back to the position before the problem arose. In Linux Mint Cinnamon we use TimeShift. The process can run fully automatically after an initial setting, where you can indicate how often a backup is made and also how long it should be kept. For example, you can set 1 time per day, 2 times per week, 1 time per month and 3 times per year to be saved, so that you can always restore to a properly working environment. To set up this process, a Linux partition, with Linux file system Ext4, must be created on an external medium or on an internal partition for the backup archive. Versions are saved next to each other, so that you can go back to any date or time, if this version exists.
 |
|
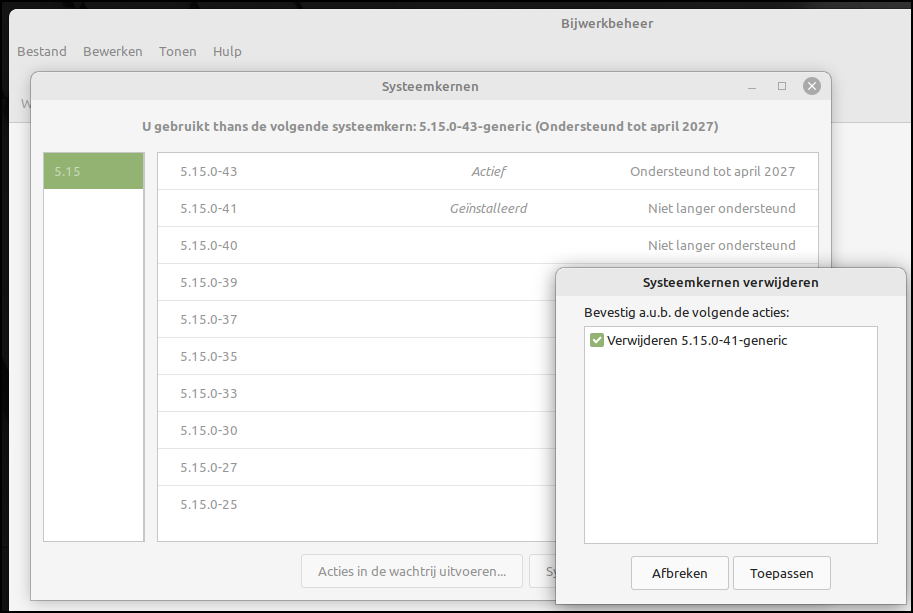
To edit the menu yourself, open the menu editor |
Menu management
In Linux Mint Cinnamon, when we install new applications through the secure software environment, the so-called Repository, the menu items are automatically created and also placed in the correct category. Games then come into the category Games and audio programs in the category Sound & Video. If we want to change this layout ourselves or add new menu items ourselves, then we can – via a right click on the start menu icon via Set up, tab Menu, Open the menu editor – these adjustments are made.
Desktop management
If you want another photo or a slide presentation as worksheet background, you can achieve this by right-clicking on the empty desktop. The choice for Pictures or slideshow can you enter Settings to make.
If you also want to install the desktop backgrounds from previous Linux Mint versions, you can do so through the Program Manager. This can be found via menu category Management and then choose Program management. You use ‘mint-backgrounds’ as a search criterion, after which you can click on the desired worksheet backgrounds of the chosen version and then install.
Toolbar
 |
 |
|
|
Left panel for app choice |
Right panel for control and connectivity |
The appearance of the toolbar – also called panel – can be customized. A right click on the toolbar takes you to Toolbar settings. The size of the bar can be set. You can set whether you always want to show or hide the toolbar. Bee Smart hide the toolbar disappears from view as an open window that takes up space on the screen.
Worksheets
Linux has the ability to work with different worksheets. One can use this to run different applications side by side, as if you were working with more physical displays. For example, you place an open internet browser on worksheet 1 and a spreadsheet application on worksheet 2. Pressing CTRL together with ALT and arrow right or arrow left lets you flip through the worksheets
 |
It is even easier to place a helper application on the toolbar. Right click on the toolbar and then choose Toolbar tools takes you to the help applications. Here you will find the Worksheet changer. You add it by clicking the button +. A visual representation of the desktops is now visible in the toolbar and you can also quickly switch to the desired desktop by clicking on it.
 |
|
|
Active corners are extremely handy to have |
Active angles
Through System Settings, Active Corners can we get a desktop overview, through a swipe gesture in a corner of the screen. You then get a nice graphical representation of the available worksheets in which you can quickly find your way to an open application you are looking for.
Themes
Much of the desktop experience is determined by the theme you set. Allows window borders, icons, control buttons, mouse pointer, and desktop menu and toolbar to change color and appearance. To manage this, go to the Menuchoose your category Preferences and then Themes.
Start by choosing one first Desktop. You can go through yourself Add Remove add new themes as chosen for the theme here Cinnamox Heather.
 |
|
The Cinnamox Heather theme |
Program management
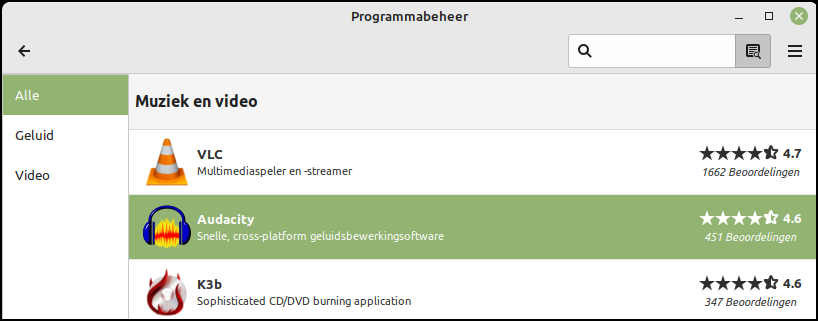
Via menu category Management and then Program management you can add a variety of additional software to the Linux Mint Cinnamon environment. In the program manager we also find the categories that we have already encountered in the menu manager. We can now search for a desired program directly or via category. If you want to edit music recordings, you can go through category Music and Video the program Audacity find. Clicking on this will bring up a short English description of the program and a button to install. Via the red button remove If the program is not what you want, you can also remove it immediately.
 |
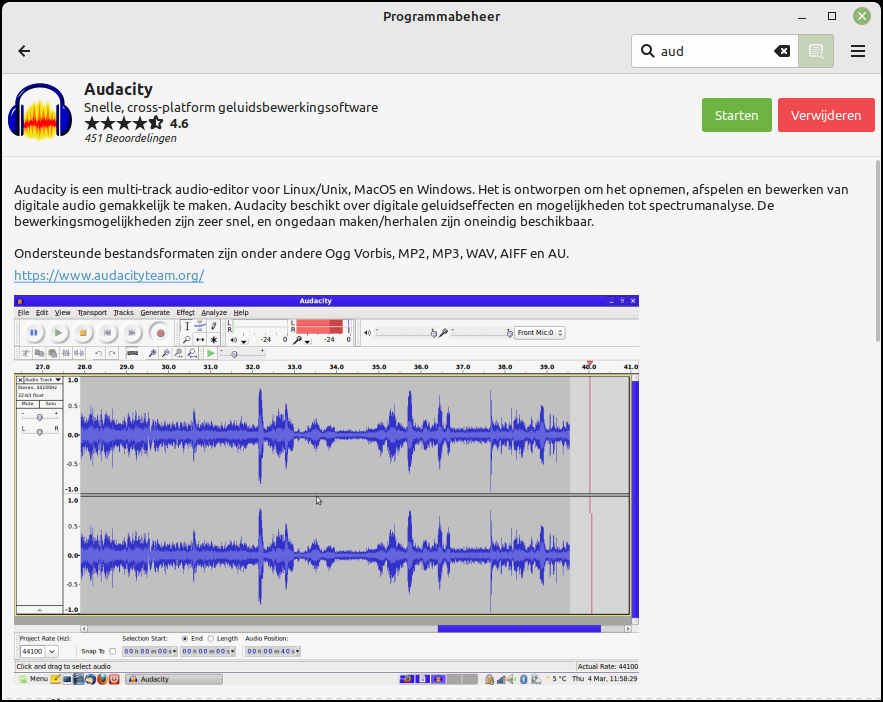 |
|
You install a sound editing program with Program Manager |
In Linux, you are always prompted for the administrator password. This prevents unauthorized installation on your computer. After entering this password, the installation will take place. Via the button Start we can start the program directly, but that is also possible via the menu and category Sound & Video.
Installed programs are updated during the operating system update.
Data management
Are you used to CTRL C, CTRL A, CTRL V and CTRL Z for cutting, copying, pasting, etc.?
In Cinnamon’s explorer Nemo it works exactly the same. In Linux Mint, you can also copy and paste the content with the comfort of the mouse. How it works: The left button of the mouse selects and the middle button or wheel pastes. It’s that simple! Function key F3 splits the screen into two parts, as if two explorers were open at the same time. This makes selecting and dragging files and folders from one place to another even easier.
Back in Time
How do you ensure that your data is protected? It is best to save the data on an external medium. The program Back in Time can make backups based on a differential method, i.e. only new and changed files are saved in the backup archive.
To unmodified files, a so-called hard link referenced, so that a full back-up is always available in case of calamities. Back in Time puts its backup archive on a Linux partition with an EXT4 Linux file system. This can also be done in addition to the TimeShift system backup on the same disk.
Explained
|
In Settings it is recorded where the backup copies, or the archive, are located.
Make sure that the archive partition for starting Back In Time is connected and open:
 An external USB drive will open automatically after physically connecting it.
An external USB drive will open automatically after physically connecting it.
A schedule can also be made to make an automatic backup under certain conditions. To do this, the Back in Time software must be started and the computer must be switched on. On the left side of the Back in Time screen is the list of all backups made. To restore something from the past, this is still possible over a longer period of time. Even when it comes to restoring a single file.